Germinal Matrix Bloeding
It is a fragile portion of th In anatomy the germinal matrix is a highly cellular and highly vascularized region in the brain out from which cells migrate during brain development. The most commonly used system is the sonographic grading system proposed by Burstein Papile et al.

Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Brain hemorrhage germinal matrix.

Germinal matrix bloeding. Germinal matrix hemorrhage is a bleeding into the subependymal germinal matrix with or without subsequent rupture into the lateral ventricle. Germinal matrix a structure in the centre of the brain that manufactures brain cells. A large GMH-IVH is often complicated by posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation PHVD or parenchymal hemorrhagic infarction and is associated with an increased risk of adverse neurologic sequelae.
A common lesion that characterizes the neuropathology of germinal matrix hemorrhage-intraventricular hemorrhage is bleeding into the subependymal germinal matrix with or without subsequent rupture into the lateral ventricle see the images below. Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage -Intraventricular hemorrhage IVH is a bleed of multifactorial etiology involving the highly vascular and delicate neuro-glial precursors in the developing brain. The germinal matrix is highly vascular and is subject to hemorrhaging.
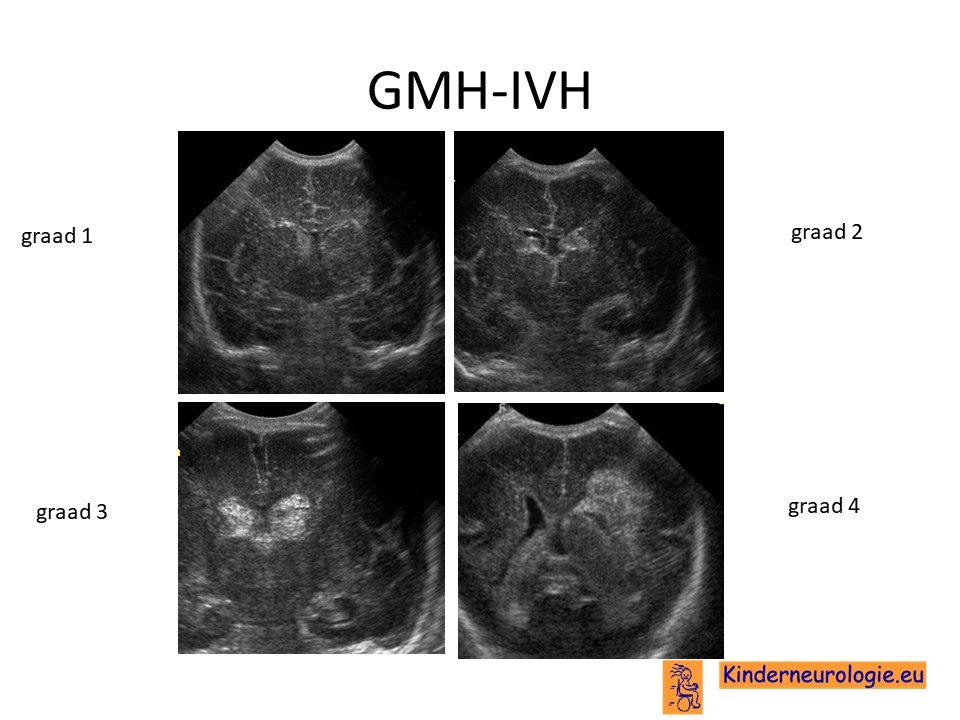
At times the bleeding will spread to other brain regions and damage the ventricles. When bleeding is limited to the germinal matrix GMH the typical CUS finding is a subependymal hyperechoic globular thickening detected during the first week of life which usually remains visible for a few weeks Fig. The germinal matrix is a thick cellular layer of immature cells neuronal and glial precursors under the ependymal lining of the ventricles.
Very low birth weight VLBW infants between 24-32 weeks gestation are most vulnerable but mature infants especially those with congenital heart disease may be affected. The hemorrhage originates from the germinal matrix with an immature capillary bed where vascularization is intense and active cell proliferation is high. When a GMH occurs it may stay confined to the matrix itself which improves chances of survival.
When bleeding is limited to the germinal matrix GMH the typical CUS finding is a subependymal hyperechoic globular thickening detected during. Such intraventricular hemorrhage can occur due to perinatal asphyxia in preterm neonates. After the ventricles have been damaged bleeding may spread to the white matter of the brain.
Also referred to as intraventricular hemorrhage IVH is an important cause of brain injury in the newborn and in particular for preterm infants. It is confined to the caudothalamic groove by 32 weeks and essentially gone by 36 weeks therefore the risk for germinal matrix hemorrhage is essentially zero in. Germinal matrix hemorrhage intraventricular hemorrhage GMH-IVH is the most common variety of neonatal intracranial hemorrhage and is characteristic of the premature infant.
This chapter provides a focused discussion on the current concepts in pathogenesis management and complications of IVH. Germinal Matrix - Intraventricular Haemorrhage. Overall good prognosis 4.
It can occur in up to 20 of infants delivered at less than 32 weeks gestation. Grading of germinal matrix hemorrhage has taken several forms over the years. Restricted to subependymal regiongerminal matrix which is seen in the caudothalamic groove.
The germinal matrix lies within the caudothalamic groove the space between the caudate head and the thalamus. Babies who are born prematurely may be unable to regulate the brains blood flow adequately so changes in pressure may occur which burst the germinal matrix blood vessels. Such intraventricular hemorrhage can occur due to perinatal asphyxia in preterm neonates.
Germinal matrix hemorrhage is bleeding which occurs inside the brain of a preterm baby. Germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage GM-IVH is a major complication of prematurity and inversely associated with gestational age and birth weight. Germinal matrix hemorrhage and intraventricular hemorrhages GMH-IVH remain a common and clinically significant problem in preterm infants particularly extremely preterm infants.
Germinal Matrix-Intraventricular Haemorrhage GM-IVH is the most common form of intracranial haemorrhage in preterm infants. The germinal matrix is a highly vascularized subependymal structure that is at risk for bleeding as a result of perinatal stress. Germinal matrix hemorrhage is a bleeding into the subependymal germinal matrix with or without subsequent rupture into the lateral ventricle.
In anatomy the germinal matrix is a highly cellular and highly vascularized region in the brain out from which cells migrate during brain developmentThe germinal matrix is the source of both neurons and glial cells and is most active between 8 and 28 weeks gestationIt is a fragile portion of the brain that may be damaged leading to a germinal matrix hemorrhage grade 1 intraventricular. The germinal matrix is an area of the brain which contains many blood vessels. The germinal matrix is the source of both.
Germinal matrix hemorrhage appears asaparenchymal collection ofblood adjacent totheforamen ofMonroe andhasaconvex margin laterally. Although the incidence has declined since the 1980s GMH-IVH remains a significant problem as improved survival of extremely preterm. This form of brain injury affects around 25 of all very low birthweight.
It typically involutes by term but is still present in premature infants. It poses a challenging complication in preterm newborns. Periventricular leukomalacia PVL is a form of ischemic white matter lesion which affects premature infants especially ones with cardiorespiratory abnormalities and sepsis.
This layer is traversed by a rich network of delicate vessels that have no structural support and lack autoregulation which makes them. The germinal matrix helps to create the fully-formed brain. Germinal matrix hemorrhage and intraventricular hemorrhage GMH-IVH.
The germinal matrix regresses in the third trimester. Tivity andaccuracy indetecting germinal matrix hemor-rhage and intraventricular hemorrhage were found. The germinal matrix is a fetal structure that is a stem source for neuroblasts.

Ppt Kan Schedel Echografie De Neurologische Outcome Voorspellen Bij Premature Neonaten Powerpoint Presentation Id 3356869

Natural Hair Colour Pigment Melanin Is Produced Within The Germinal Matrix Of The Hair Bulb By Cells Calle Hair Color Natural Hair Color Integumentary System

Intraventriculaire Bloeding Wikipedia

Intracranial Hemorrhage In The Newborn Intracranial Hemorrhage Hemorrhage Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Grade Ii Intraventricular Hemorrhage The Image On The Left Is A Coronal Image Of The Brain Showing Diagnostic Medical Sonography Ultrasound School Sonography

Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Brain Mri 8 Day Old With A Bleed Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Radiologist This Information Is F Protected Health Information Radiology Mri
Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Intraventricular Hemorrhage Obstetric Ultrasound Medical Ultrasound Ultrasound

Grading Of Germinal Matrix Haemorrhage Literature Can Only Occur When The Germinal Matrix Is Present And Is Therefore Only Ultrasound Hemorrhage Pediatrics

Germinal Matrix Caudate Nucleus Face Home Decor Decals

Germinal Matrix Haemorrhage Left Subependymal Oval Shape Hematoma With Averagey Density Of 65 Hu Seen Adjacent To Fora Hemorrhage Radiology Imaging Radiology